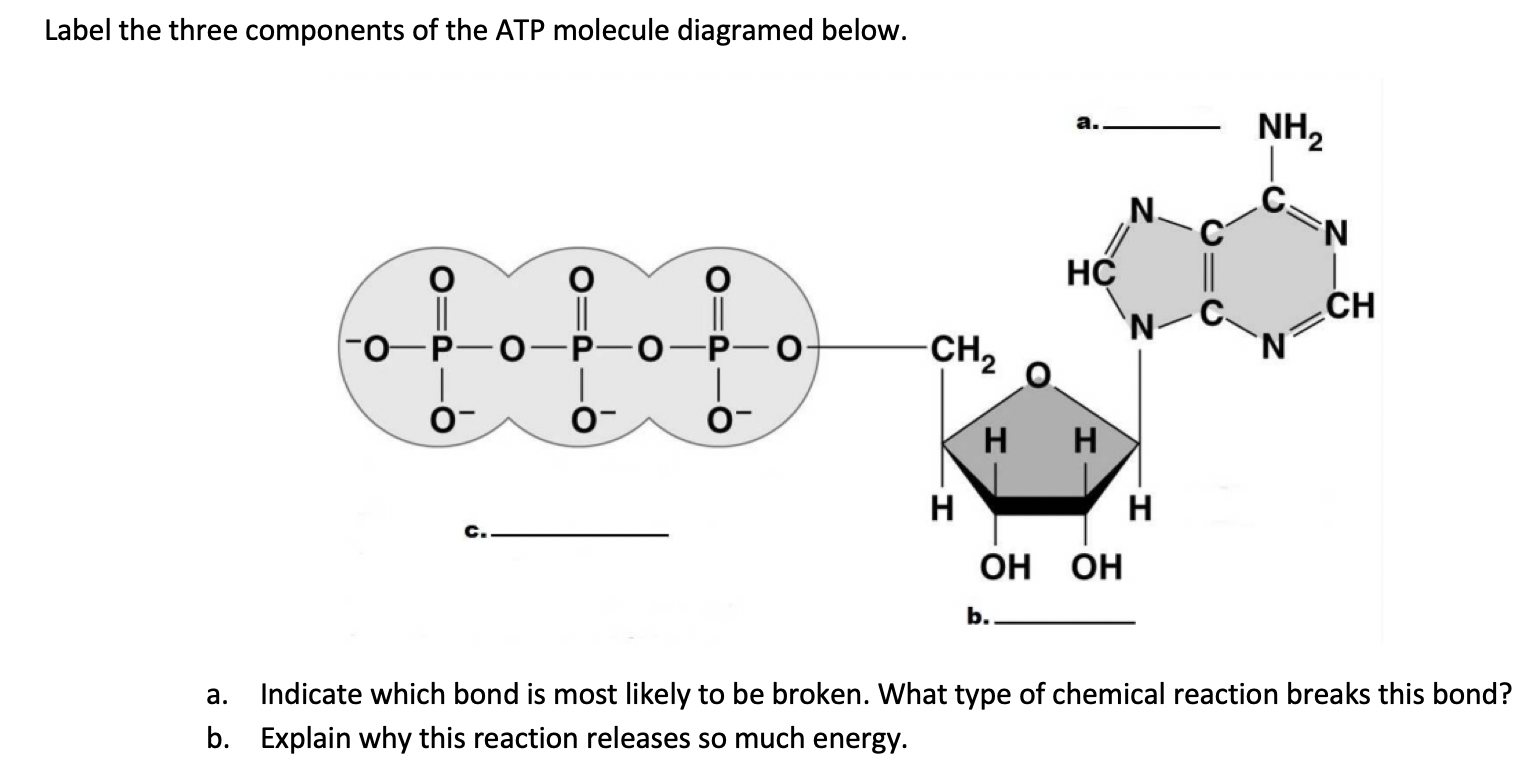
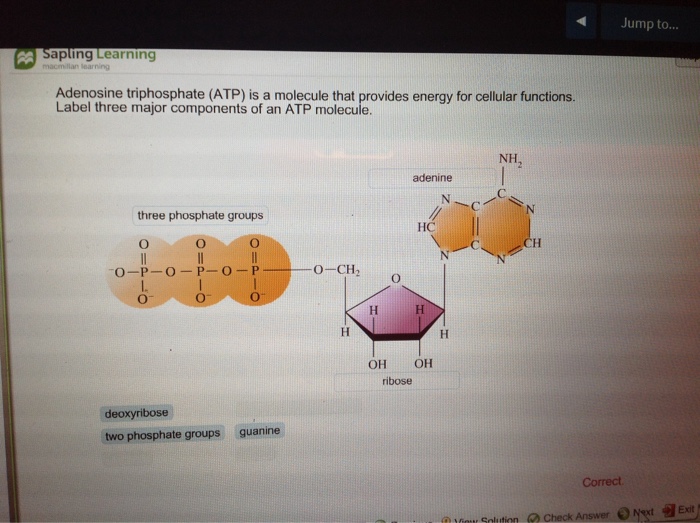
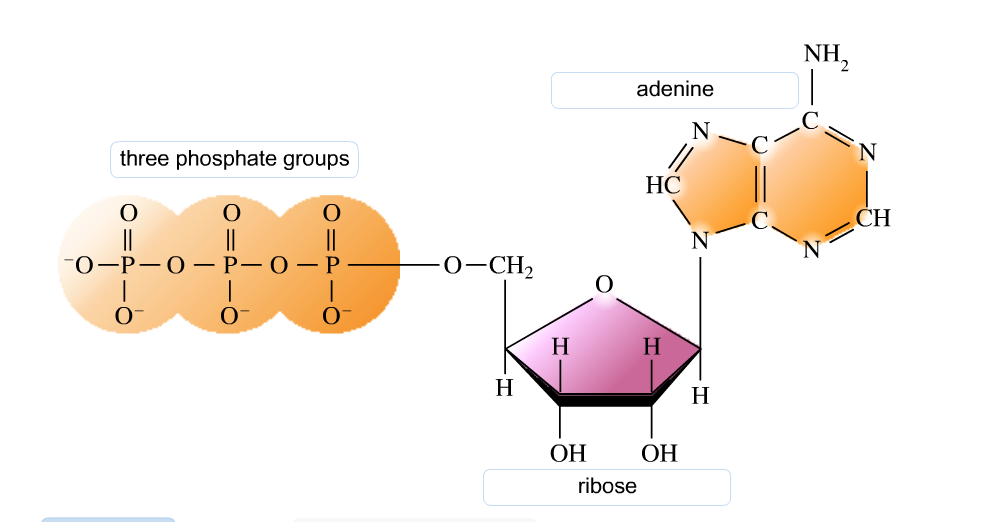
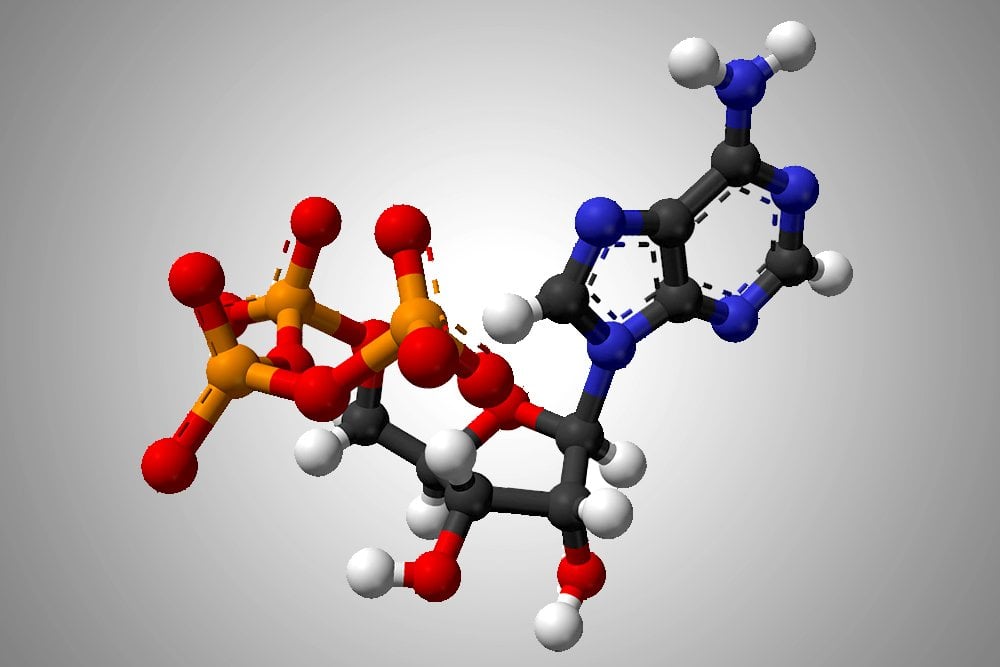
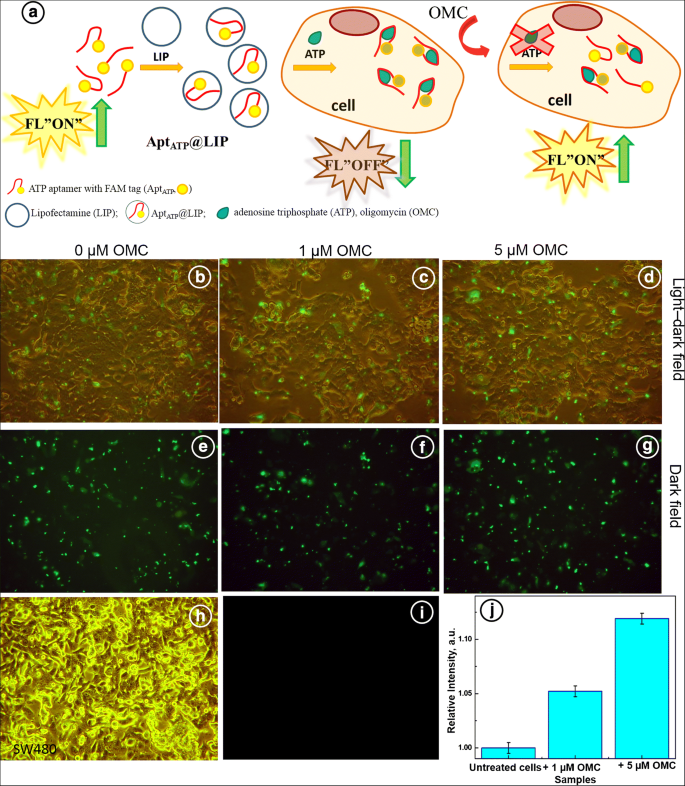
41 adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. label the three major components of an atp molecule.
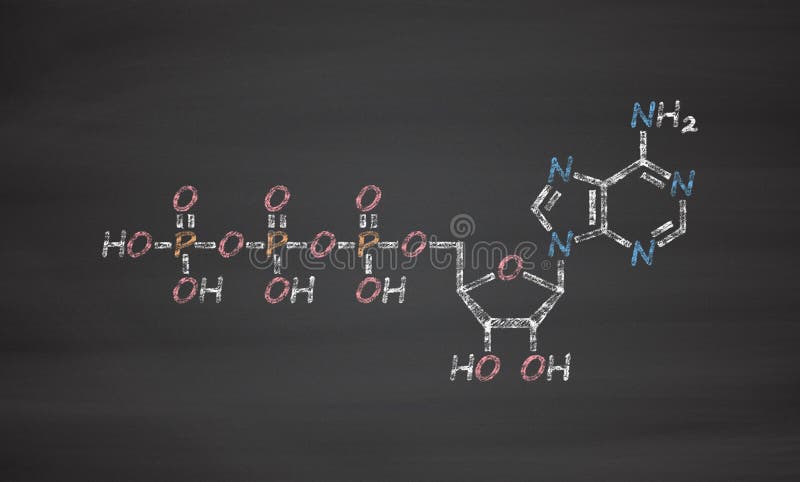
Physiology, Adenosine Triphosphate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The body is a complex organism, and as such, it takes energy to maintain proper functioning. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups. ATP is commonly referred to as the "energy currency ... (Solved) - The highest-energy phosphate bond in ATP is ... - Transtutors Answer: (E) Two phosphate ...
ATP Definition and Importance in Metabolism - ThoughtCo Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is often called the energy currency of the cell because this molecule plays a key role in metabolism, particularly in energy transfer within cells. The molecule acts to couple the energy of exergonic and endergonic processes, making energetically unfavorable chemical reactions able to proceed.
Adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. label the three major components of an atp molecule.
ATP Overview & Uses | What Does ATP Stand For? - Study.com ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate. ATP definition: ATP is a high-energy molecule that can be found in all types of cells, including plant cells, muscle cells, nerve cells, and more. ATP is... Solved Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that - Chegg Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. NH, Answer Bank guanine three phosphate groups v=CH deoxyribose adenine -O-P-0 - P-0 — -0-CH ribose k H H two phosphate groups ОН ОН Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts ...
Adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. label the three major components of an atp molecule.. What is adenosine triphosphate? - Quora Answer (1 of 3): What is adenosine triphosphate? Adenosine triphosphate is ATP, and is often called the energy currency of the cell. As the name indicates, it consists of the nucleoside adenosine plus 3 phosphates. Adenosine itself is composed of the nitrogenous base adenine plus the pentose ri... Adenosine Triphosphate - GSU Free Energy from Hydrolysis of ATP Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency of life and it provides that energy for most biological processes by being converted to ADP (adenosine diphosphate). Since the basic reaction involves a water molecule, ATP + H 2 O → ADP + P i. this reaction is commonly referred to as the hydrolysis of ATP.The change in Gibbs free energy in the reaction is ... Understanding ATP—10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered The initials ATP stand for adenosine tri-phosphate. This long name translates to a nucleic acid (protein) attached to a sugar and phosphate chain. Phosphate chains are groups of phosphorous and oxygen atoms linked together. One cool fact: ATP closely resembles the proteins found in genetic material. 3. How Does ATP Carry Energy? Solved Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that - Chegg Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions Label three major components of an ATP molecule NH, C. CH OmCH FT OH OH ribose deoxyribose guanine wo phosphate groups three phosphate groups adenine
How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com ADP also called adenosine diphosphate, is a molecule formed in living cells. It is often converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a high-energy molecule used in various biochemical reactions. ADP... Adenosine Triphosphate - Bristol The ATP molecule is composed of three components. At the centre is a sugar molecule, ribose (the same sugar that forms the basis of RNA). Attached to one side of this is a base (a group consisting of linked rings of carbon and nitrogen atoms); in this case the base is adenine. The other side of the sugar is attached to a string of phosphate groups. The Three Primary Energy Pathways Explained - American Council on Exercise However, we cannot use energy directly from food—it must first be converted into adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, the immediate useable form of chemical energy utilized for all cellular function. The body does store a minimal amount of ATP within the muscles, but the majority is synthesized from the foods we eat. ATP+Video+Questions.docx - Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: ATP... Refer to diagram for Label of ATP ATP is a nucleotide.Its initials stand for adenosine triphosphate, which indicates that it contains the nitrogenous base adenine/adenosine, the pentose sugar ribose and three phosphate groups.These components are linked together into a single molecule through condensation reactions.
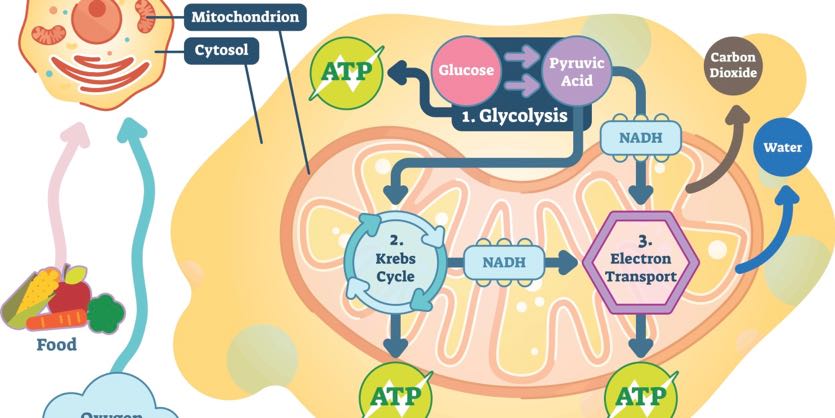
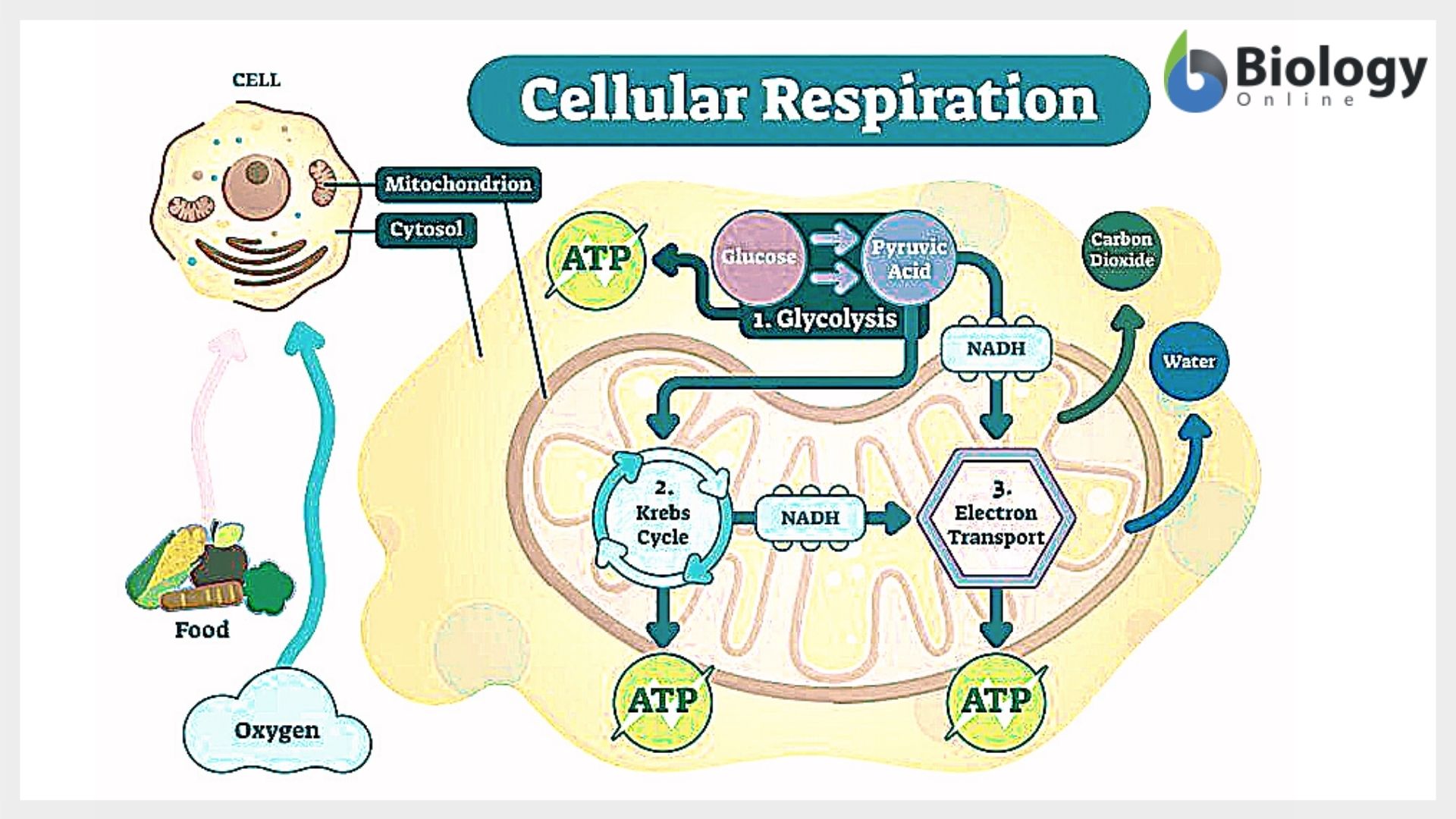
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. ATP - powering the cell - Cellular respiration - BBC Bitesize ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy-carrying molecule used in cells because it can release energy very quickly. Energy is released from ATP when the end phosphate is removed. Once ATP has... What Is ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) and What Does It Do? - LuminUltra Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is the primary energy carrier in all living organisms on earth. Microorganisms capture and store energy metabolized from food and light sources in the form of ATP. When the cell requires energy, ATP is broken down through hydrolysis. The high energy bond is broken and a phosphoryl group is removed. Learn About the 3 Main Stages of Cellular Respiration - ThoughtCo We all need energy to function, and we get that energy from the foods we eat. Extracting those nutrients necessary to keep us going and then converting them into useable energy is the job of our cells.This complex yet efficient metabolic process, called cellular respiration, converts the energy derived from sugars, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, a high ...
BIOL 1408 SAPLING CH 4 HW Flashcards | Quizlet ATP Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. (top) adenine (middle) three phosphate groups (bottom) ribose a carbohydrate that enters glycolysis directly glucose the direct energy source for glycolysis ATP
adenosine triphosphate | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts small organic molecules including adenosine triphosphate ATP is a nucleotide that consists of three main structures: the nitrogenous base, adenine; the sugar, ribose; and a chain of three phosphate groups bound to ribose. The phosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source which the cell taps.
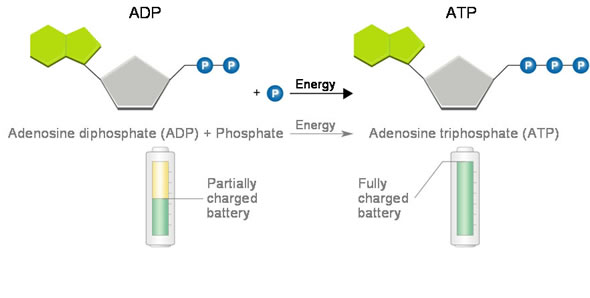
ATP AND BIOLOGICAL ENERGY - Estrella Mountain Community College This covalent bond is known as a pyrophosphate bond. We can write the chemical reaction for the formation of ATP as: a) in chemicalese: ADP + Pi + energy ----> ATP. b) in English: Adenosine diphosphate + inorganic Phosphate + energy produces Adenosine Triphosphate. The chemical formula for the expenditure/release of ATP energy can be written as ...
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: Answer link
Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. three phosphate,ribose,adenine Classify the following statements about the structure of an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule as true or false. Reminder: Adenosine diphosphate is abbreviated ADP.
Cellular Respiration - Definition, Equation and Steps - Biology Dictionary ATP. The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This molecule stores the energy released during respiration and allows the cell to transfer this energy to various parts of the cell. ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy. For example, an enzyme may need energy from ...
Adenosine triphosphate - American Chemical Society Specifically, it is a coenzyme that works with enzymes such as ATP triphosphatase to transfer energy to cells by releasing its phosphate groups. The molecule consists of three components: an adenine bicyclic system, a furanose ring, and a triphosphate chain. Two research groups reported the discovery of ATP in 1929.
ATP - Energy Currency of the Cell - Structure and its Functions - BYJUS ATP - Adenosine triphosphate is called the energy currency of the cell. It is the organic compound composed of the phosphate groups, adenine, and the sugar ribose. These molecules provide energy for various biochemical processes in the body. Therefore, it is called "Energy Currency of the Cell".
Adenosine triphosphate - WikiMili, The Best Wikipedia Reader Interactive animation of the structure of ATP. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound and hydrotrope that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular ...
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate | Boundless Biology | | Course Hero Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency for cellular processes. ATP provides the energy for both energy-consuming endergonic reactions and energy-releasing exergonic reactions, which require a small input of activation energy. When the chemical bonds within ATP are broken, energy is released and can be harnessed for cellular work.
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts ...
Solved Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that - Chegg Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. NH, Answer Bank guanine three phosphate groups v=CH deoxyribose adenine -O-P-0 - P-0 — -0-CH ribose k H H two phosphate groups ОН ОН
ATP Overview & Uses | What Does ATP Stand For? - Study.com ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate. ATP definition: ATP is a high-energy molecule that can be found in all types of cells, including plant cells, muscle cells, nerve cells, and more. ATP is...




















Post a Comment for "41 adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. label the three major components of an atp molecule."