38 simple diagram of a single nucleotide
Reproduction, the genome and gene expression - BBC Bitesize Each nucleotide consists of alternating sugar and phosphate sections with one of the four different bases attached to the sugar. Base pairs Each strand of DNA is made of chemicals called bases.... Polynucleotide Chain Structure & Overview - Study.com Schematic diagram of chemical structure of a polynucleotide (DNA) chain showing sugar-phosphate backbone and hydrogen bonds between complementary bases. Functions of a Polynucleotide Chain
DNA and RNA - BIOLOGY FOR LIFE Explain how Watson and Crick used model building to determine the structure of DNA. 2.6.S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons, and rectangles to represent phosphates, pentoses and bases. Draw the basic structure of a single nucleotide (using circle, pentagon and rectangle).
Simple diagram of a single nucleotide
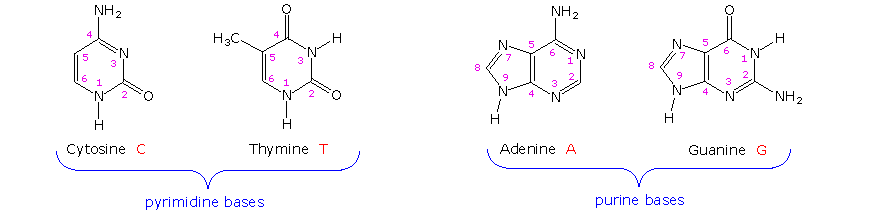
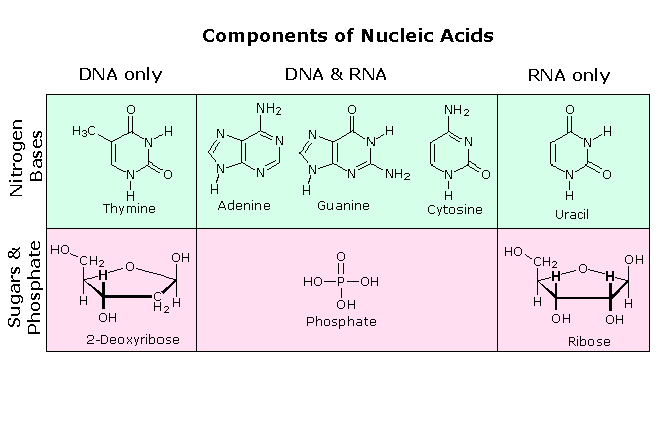
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected - ThoughtCo Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. In DNA, the bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). In RNA, the bases are adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. Pentose Sugar In DNA, the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose. In RNA, the sugar is ribose. Both ribose and deoxyribose are 5-carbon sugars. Nucleotides | BioNinja Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, pentoses and bases AND The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides ... Each nucleotide is comprised of three principal components: 5-carbon pentose sugar (pentagon) Phosphate group (circle) › about-genomics › fact-sheetsDeoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Fact Sheet - Genome.gov Aug 24, 2020 · So, if you know the sequence of the bases on one strand of a DNA double helix, it is a simple matter to figure out the sequence of bases on the other strand. DNA's unique structure enables the molecule to copy itself during cell division. When a cell prepares to divide, the DNA helix splits down the middle and becomes two single strands.
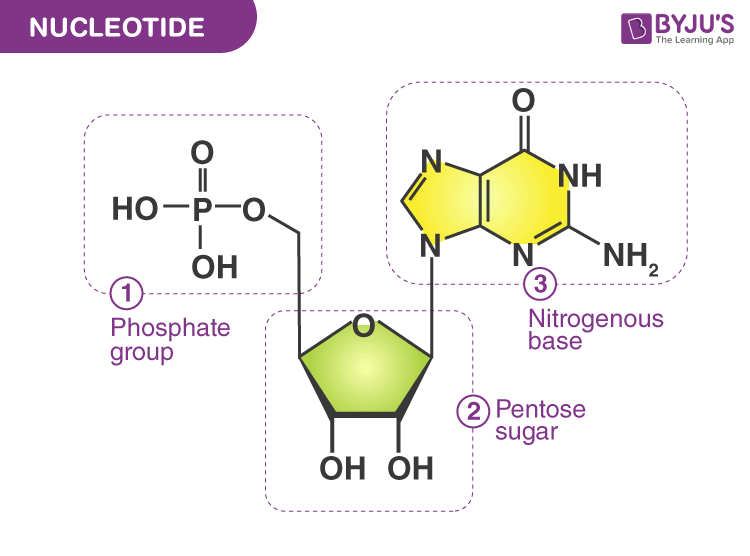
Simple diagram of a single nucleotide. Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS A nucleotide consists of three units, which are covalently linked. They are: Nitrogenous bases - Purine and Pyrimidine Pentose Sugar - Ribose and Deoxyribose Phosphate - monophosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate 1. Nitrogenous Base: They comprise pyrimidine or purine base. › indexPHSchool.com Retirement–Prentice Hall–Savvas Learning Company PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobe’s decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support. Nucleotide: Structure, Bonding & Mutations - Study.com Nucleotide Structure. Nucleotides are the monomers (or the building blocks) of nucleic acids and are made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Notice in the diagram ... 3.3.5 Draw a simple diagram of DNA structure - YouTube 3.3.5 Draw and label a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA. Here I demonstrate drawing the structure of DNA. You don't need to be an artist, its relative positions of the phosphate...
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram - Science Trends As mentioned, nucleotides have three component parts: a five-sided carbon sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group. The sugar and phosphate group together to create the sugar phosphate backbone. This is skeleton or foundation of the DNA double helix. Single-nucleotide polymorphism - Wikipedia A tag SNP is a representative single-nucleotide polymorphism in a region of the genome with high linkage disequilibrium (the non-random association of alleles at two or more loci). Tag SNPs are useful in whole-genome SNP association studies, in which hundreds of thousands of SNPs across the entire genome are genotyped. Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification One nitrogenous base is attached to the first carbon of a pentose sugar to form a nucleoside. The addition of a phosphate group to a nucleoside makes it nucleotide. Phosphate Groups These are the third essential component of a nucleotide. Phosphate groups are simply phosphate ions made up of a phosphorus atom bound to four oxygen atoms (PO 43- ). Nucleotide - Wikipedia Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar ( ribose or deoxyribose ), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine.
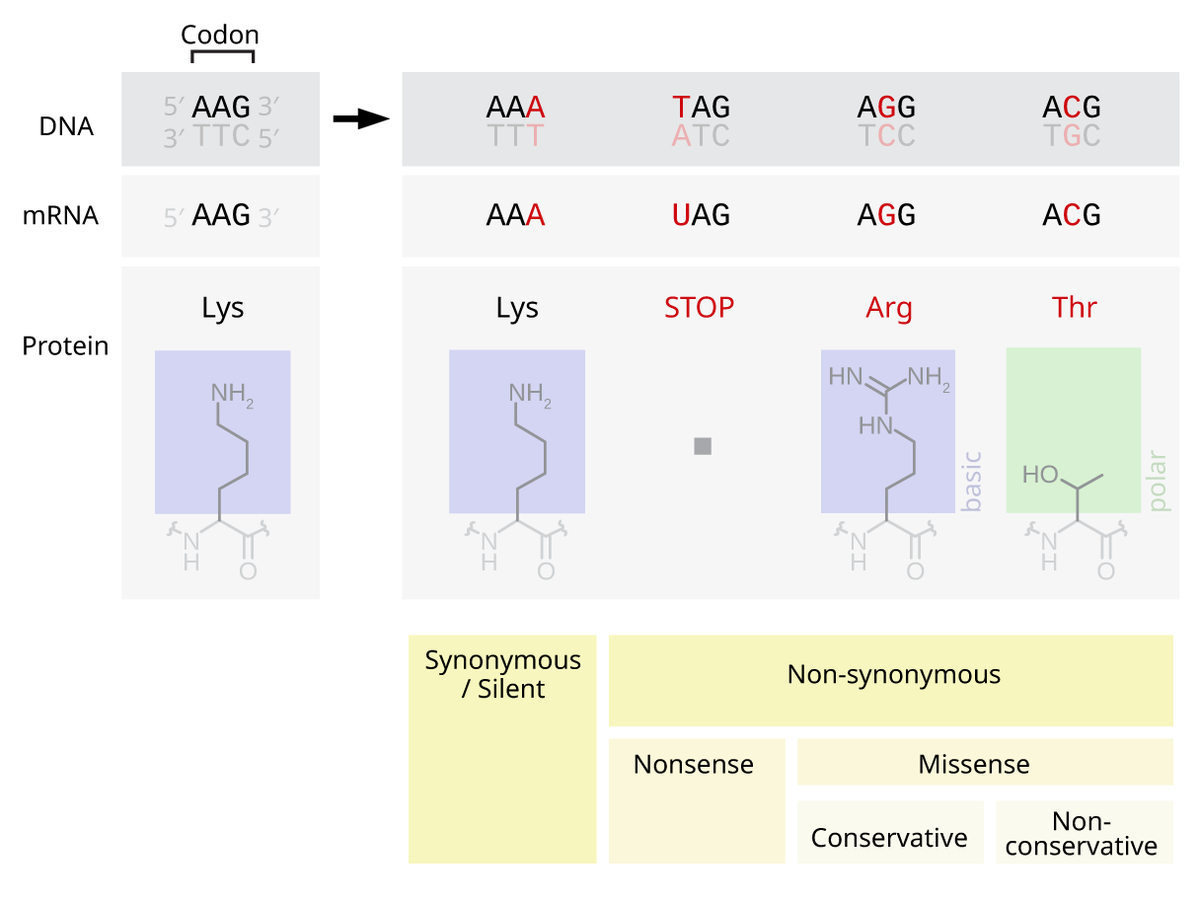
Solved Label the diagram of a single nucleotide. Only three - Chegg Label the diagram of a single nucleotide. Only three labels will be used. Nucleotide NH2 4-carbon sugar N H- N Amine group b=0 HO-P-0-CH2 OH 5-carbon sugar H OHH Phosphate group Nucleobase Which regions of the gene for segment of DNA) shown here encodes the amino acid sequence of a protein? How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group 5-carbon sugar, and nitrogenous base. Answer link DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Base_pairBase pair - Wikipedia An unnatural base pair (UBP) is a designed subunit (or nucleobase) of DNA which is created in a laboratory and does not occur in nature. DNA sequences have been described which use newly created nucleobases to form a third base pair, in addition to the two base pairs found in nature, A-T (adenine – thymine) and G-C (guanine – cytosine).
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Fluorescence_microscopeFluorescence microscope - Wikipedia "Fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image.
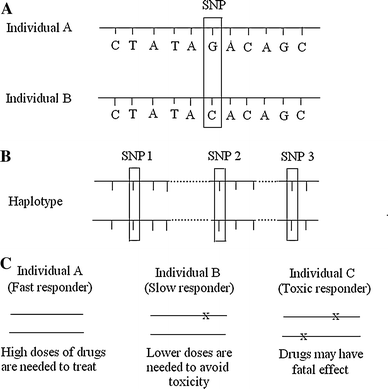
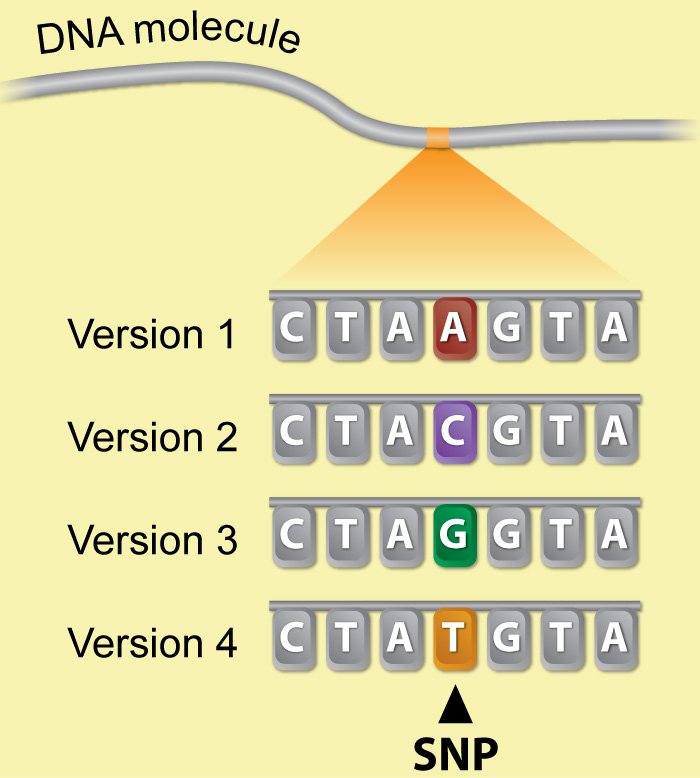
Single-nucleotide polymorphism - ISOGG Wiki A single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP, pronounced snip) is a DNA sequence variation occurring when a single nucleotide adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G]) in the genome (or other shared sequence) differs between members of a species or paired chromosomes in an individual. For example, two sequenced DNA fragments from different individuals, AAGCCTA to AAGCTTA, contain a ...
topic 2.6: structure of dna and rna - AMAZING WORLD OF SCIENCE WITH MR ... Draw the basic structure of a single nucleotide (using circle, pentagon and rectangle). Draw a simple diagram of the structure of RNA. Draw a simple diagram of the structure of DNA. Identify and label the 5' and 3' ends on a DNA or RNA diagram Both the phosphate group and nitrogenous base are attached to the central pentose sugar
Solved The diagram depicts the general structure of DNA, | Chegg.com Question: The diagram depicts the general structure of DNA, with a single nucleotide circled. Label the diagram with the names of the three components of a nucleotide Anwer Bank nitrogenous base phosphate group deutytibes This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts.
› lifestyleLifestyle | Daily Life | News | The Sydney Morning Herald The latest Lifestyle | Daily Life news, tips, opinion and advice from The Sydney Morning Herald covering life and relationships, beauty, fashion, health & wellbeing
Draw And Label A Single Dna Nucleotide / Draw And Label Schematic ... Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of dna and rna, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, pentoses and . Nucleic acids are made up of chains of many repeating units called nucleotides (see bottom left of figure 1 below). The above structure is a .
IB Biology Notes - 3.3 DNA structure - IB Guides Below is a diagram showing how nucleotides are linked to one another to form a strand. A covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate group of another nucleotide. 3.3.4 Explain how a DNA double helix is formed using complementary base pairing and hydrogen bonds. DNA is made up of two nucleotide strands.
› projects › fastqcBabraham Bioinformatics - FastQC A Quality Control tool for ... FastQC aims to provide a simple way to do some quality control checks on raw sequence data coming from high throughput sequencing pipelines. It provides a modular set of analyses which you can use to give a quick impression of whether your data has any problems of which you should be aware before doing any further analysis.
2.6: DNA and RNA Flashcards | Quizlet A nucleotide is the monomer subunit of the nucleic acids. A nucleotide has three component parts: 1. a nitrogenous base 2. A 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) 3. A phosphate group Identify and label carbons by number (for example, C1, C2, C3) on a nucleotide drawing. Understanding: The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides.
Topic 2.6 Skill 1 Drawing Simple Diagram of Nucleotide, Dna and Rna Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons, and rectangles to represent phosphates, pentoses, an...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › GenomeGenome - Wikipedia In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses).The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident ...
The Structure of DNA - University of Arizona Alternating sugar and phosphate units form the two sides of a ladder-shaped arrangement with the rungs or steps each formed by a pair of nucleotide bases. Figure 2 below shows the structural formula of DNA in greater detail. The nitrogen bases are ring compounds with their carbon and nitrogen atoms arranged in single or double rings.
Nucleotide - Genome A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine.
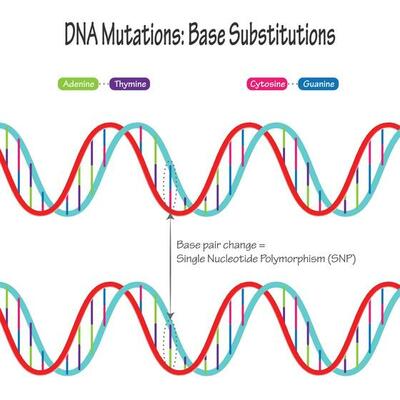
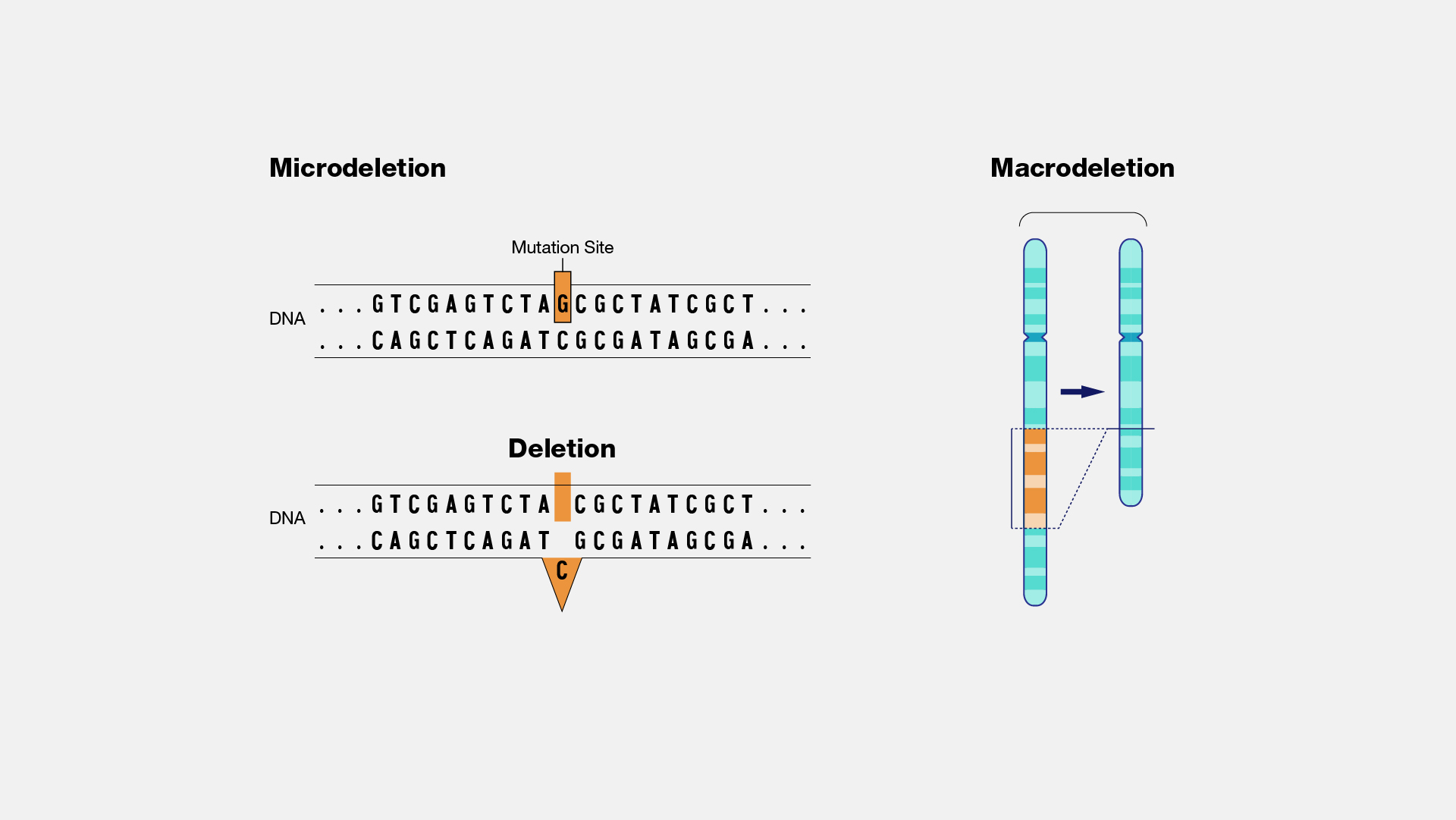
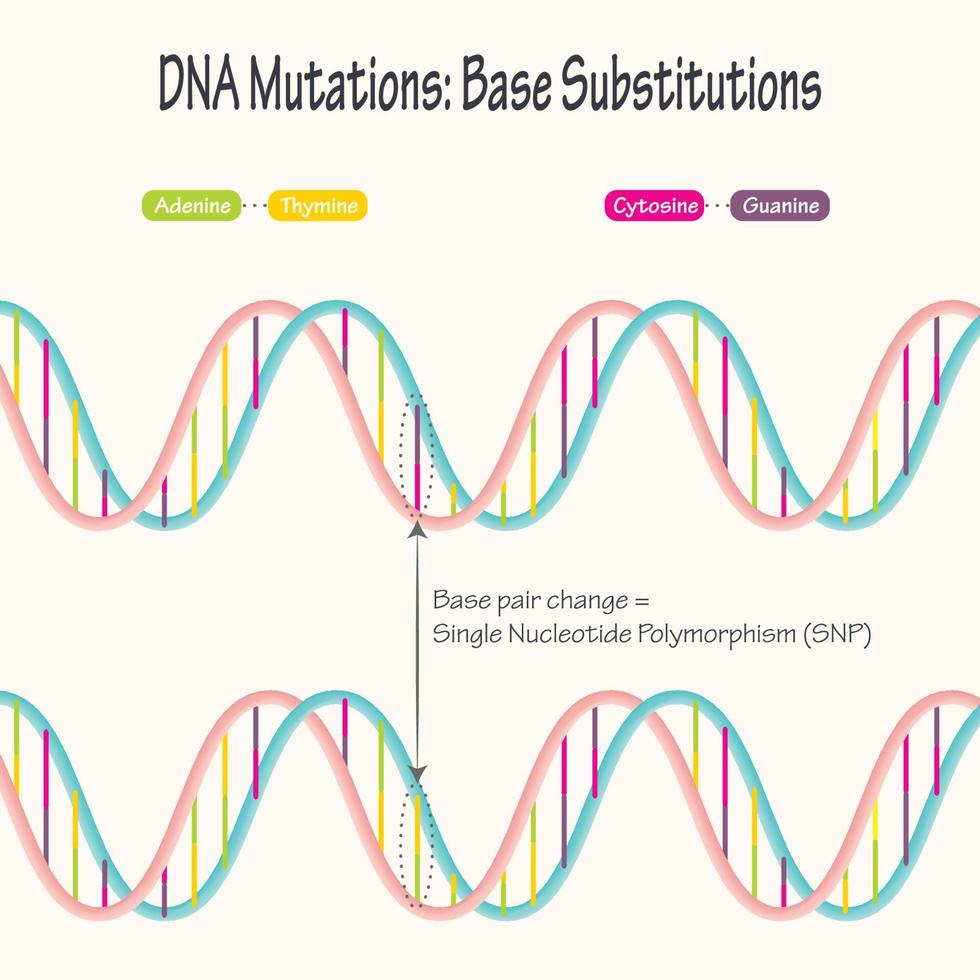
An Introduction To Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) - Genetic Education SNP is one of a kind of genetic mutation/ alteration which arises due to addition or deletion of a single nucleotide into the DNA sequence. Due to the adverse environmental conditions, stress and unhealthy lifestyle many single nucleotide alterations are inserted or deleted in a genome . In a population, if a specific SNP, at specific location ...
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Single nucleotide polymorphisms, frequently called SNPs (pronounced "snips"), are the most common type of genetic variation. Each SNP represents a difference in a single DNA building block, called a "nucleotide." ... For a simple stain DNA analysis, a set of 50-100 SNPs is as powerful as a set of 10 STRs. For mixtures, however, the ...
What are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)? - MedlinePlus Single nucleotide polymorphisms, frequently called SNPs (pronounced "snips"), are the most common type of genetic variation among people. Each SNP represents a difference in a single DNA building block, called a nucleotide. For example, a SNP may replace the nucleotide cytosine (C) with the nucleotide thymine (T) in a certain stretch of DNA.
› about-genomics › fact-sheetsDeoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Fact Sheet - Genome.gov Aug 24, 2020 · So, if you know the sequence of the bases on one strand of a DNA double helix, it is a simple matter to figure out the sequence of bases on the other strand. DNA's unique structure enables the molecule to copy itself during cell division. When a cell prepares to divide, the DNA helix splits down the middle and becomes two single strands.
Nucleotides | BioNinja Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, pentoses and bases AND The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides ... Each nucleotide is comprised of three principal components: 5-carbon pentose sugar (pentagon) Phosphate group (circle)
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected - ThoughtCo Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. In DNA, the bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). In RNA, the bases are adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. Pentose Sugar In DNA, the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose. In RNA, the sugar is ribose. Both ribose and deoxyribose are 5-carbon sugars.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)












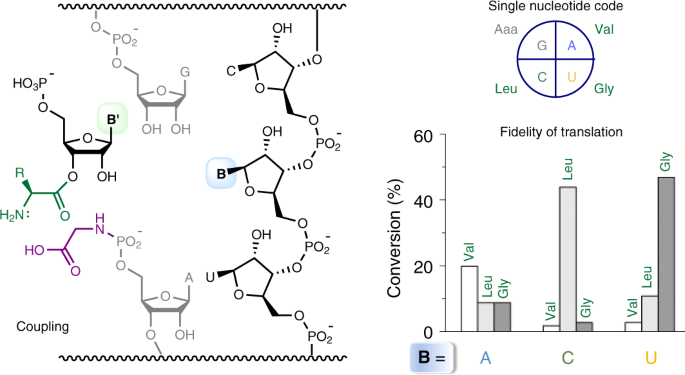


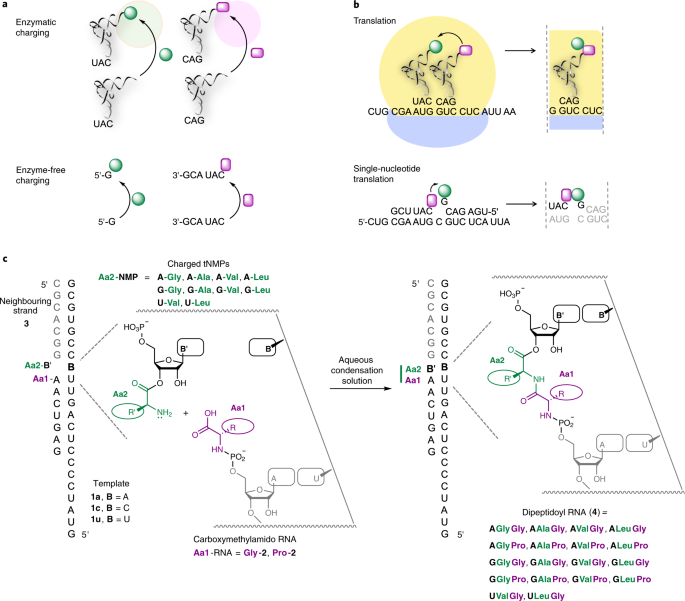






Post a Comment for "38 simple diagram of a single nucleotide"